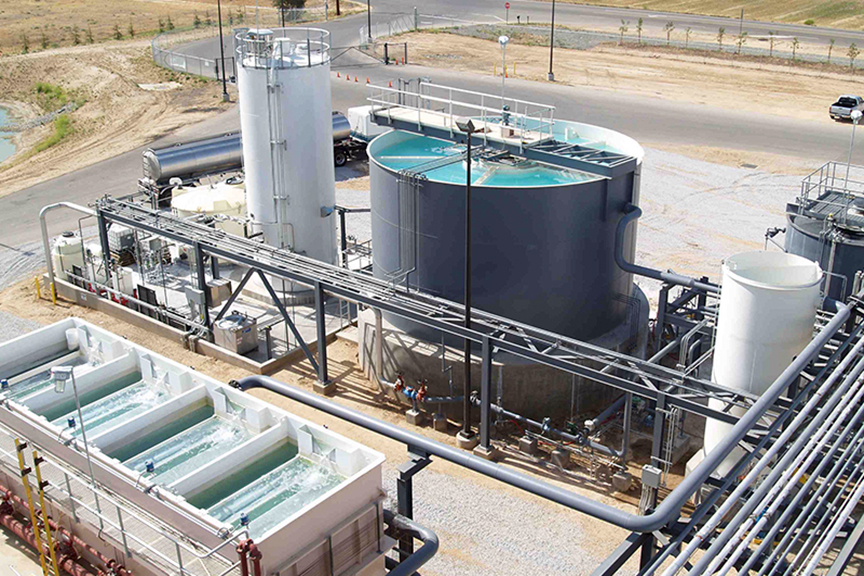
As the world grapples with growing environmental challenges, safeguarding waterways has become an urgent imperative. One vital strategy in this effort is the pursuit of “Zero Discharge,” a commitment to eliminating the release of pollutants from point sources such as buildings and processing plants into local water bodies. The significance of this topic explores multifaceted applications, and emphasizes the role of responsible water stewardship in preserving a most precious resource: water.
Understanding Zero Discharge:
Zero Discharge signifies the complete cessation of pollutant discharge from a specific source to local waterways. This ambitious goal can encompass various scenarios.
In some instances, companies and facilities aim to achieve this by eliminating all pollutants from their operations. It’s often a lofty task, but considerations taken, a step by step approach can achieve results.
Alternatively, Zero Discharge can be specific to certain pollutants. This approach emphasizes meticulous control over a particular pollutant as opposed to an overall approach. Minimizing specifics supports the overall effort, step by step.
Embracing Water Stewardship as a Key Component:
Zero Discharge isn’t just about regulatory compliance; it’s about embracing the principles of water stewardship. Being a good water steward entails understanding water use, acknowledging the context of the local watershed, and recognizing shared risks associated with water governance, quality, and availability. Water stewardship is integral to the journey.
Responsible water stewards engage in transparent and sustainable water governance practices, working closely with local communities, regulators, and stakeholders to ensure equitable and environmentally sound water management.
Achieving the overall goal often involves optimizing water use within an organization. Water stewards strive to maintain a favorable water balance, minimizing waste and maximizing water efficiency.
Preservation of water quality is paramount. Through vigilant monitoring and treatment processes, water stewards ensure that discharged water meets or exceeds established water quality standards.
Practical Applications of Zero Discharge:
Implementing positive practices involves a combination of technological innovation and responsible resource management. Some practical examples include:
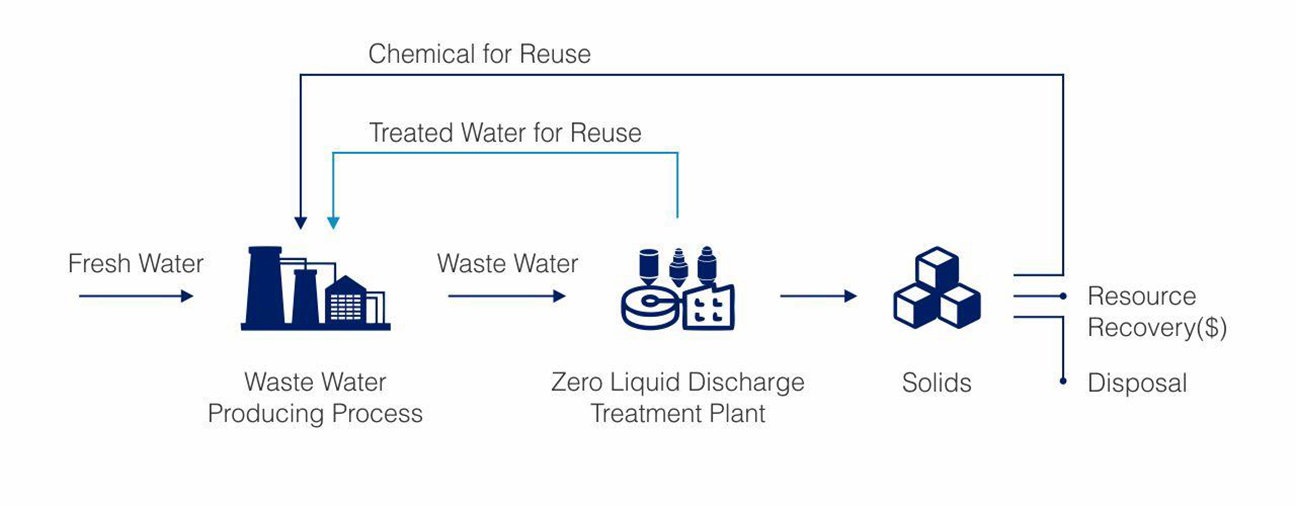
Treating wastewater to recover reusable water and concentrate potential pollutants into a solid phase (sludge) for responsible disposal. This minimizes the release of harmful substances into water bodies.
Implementing water-efficient technologies and processes helps to reduce the amount of water needed during production, thereby decreasing the volume of wastewater generated. As with any major changes, it can be a step by step approach by identifying the issues and being proactive in small increments to support the overall goal of Water Stewardship.
Zero Discharge represents a crucial step toward protecting our waterways and ensuring a sustainable future. Whether it involves comprehensive pollutant elimination or the targeted removal of specific contaminants, this commitment underscores the importance of responsible environmental stewardship. Embracing water stewardship as an integral component of Zero Discharge not only helps organizations meet their environmental responsibilities but also fosters a deeper connection to the vital resource that sustains life on Earth—water.