Amazon, the e-commerce behemoth, often touted for its convenience and vast product selection, hides a darker side that many may not be aware of. In a 2019 survey, three-quarters of independent retailers ranked Amazon’s dominance as a major threat to their survival, while only 11 percent of those selling on its platform described their experience as successful. This review delves into the predatory tactics and monopolistic practices employed by the Amazon Monopoly that have left a trail of victims in its wake.
Small Businesses and Independent Retailers:
The overwhelming dominance of the Amazon Monopoly in the e-commerce industry has had devastating effects on small retailers and independent businesses. Between 2007 and 2017, the number of small retailers fell by 65,000, and roughly 40 percent of small apparel, toy, and sporting goods makers disappeared, along with one-third of small book publishers. The vast majority of online shoppers begin their searches on Amazon, forcing businesses to sell on its platform. This dependence is risky as changes to Amazon’s search algorithms or selling terms can obliterate their sales overnight. Amazon also restricts the contact between sellers and customers, making it challenging for businesses to build relationships and brand identity.
Amazon’s Fulfillment By Amazon (FBA) Monopoly:
The Amazon Monopoly has made a seller’s ability to succeed on its platform highly contingent on subscribing to its warehousing and shipping services, known as Fulfillment By Amazon (FBA). FBA subscribers receive preferential treatment, including the coveted Prime badge, and they are more likely to be chosen by Amazon’s algorithms as the default seller. By virtually making FBA mandatory, Amazon has created a logistics empire at the expense of independent businesses that may prefer other carriers.
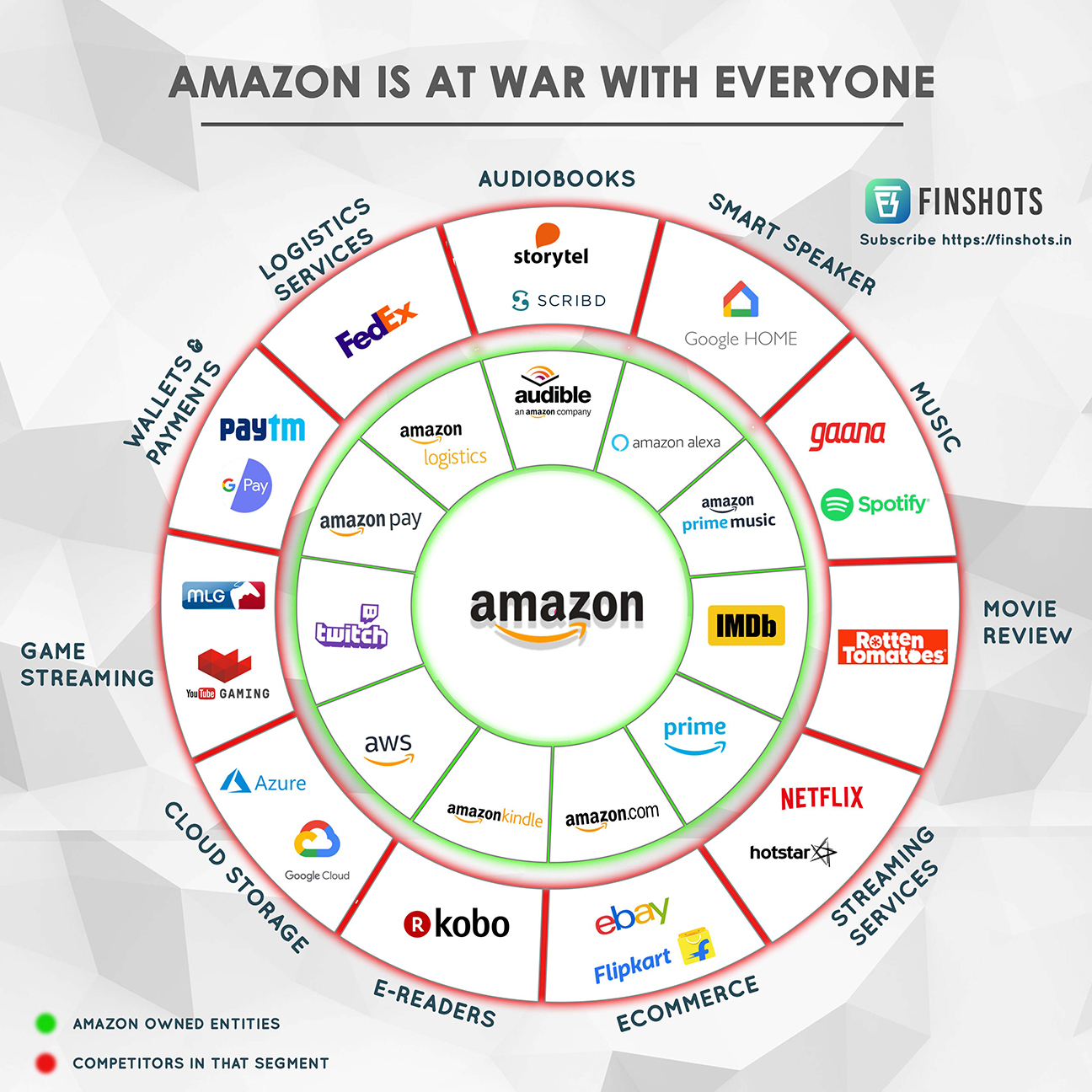
Exorbitant Seller Fees:
Amazon’s revenue from seller fees skyrocketed to $60 billion in 2019, with the tech giant extracting an average of 30 percent from each sale made by independent businesses on its platform. This rise in fees has made it nearly impossible for small sellers to sustain a profitable business. They are coerced into purchasing additional Amazon services, including shipping and advertising, to improve their visibility and sales.
Price Manipulation and Suppression:
Amazon blocks independent businesses from offering lower prices on other platforms, effectively insulating itself from competition and preserving its dominance. If Amazon’s pricing bots detect lower prices elsewhere, the seller’s sales are suppressed, causing a significant drop in sales. This strategy further cripples small businesses.
Suspensions and Arbitration:
Amazon frequently suspends sellers’ accounts and seizes their inventory and cash balances, often abruptly and arbitrarily. Sellers have little recourse, and they are forced into an arbitration process due to Amazon’s standard contract, which prohibits legal action. The arbitration process is widely criticized as unfair and unlikely to result in a meaningful remedy, leaving sellers in a precarious position.
Predatory Pricing and Bullying Tactics:
Amazon has consistently employed predatory pricing to undercut competitors and expand its market share. This strategy not only hurt bookstores during its early years but also eliminated e-commerce rivals. Small brands are strong-armed into compliance, giving Amazon even more leverage to extract price concessions and special terms. Those who resist Amazon’s demands face punitive retaliation.
While Amazon’s convenience and vast product selection have made it a household name, it’s essential to be aware of the shadowy practices that have accompanied its rise to dominance. Small businesses, independent retailers, and creators have all felt the impact of Amazon’s monopoly gambit, leaving them in a constant struggle for survival. As consumers, understanding these issues allows us to make informed choices and support businesses that uphold fair and ethical practices in the digital marketplace.