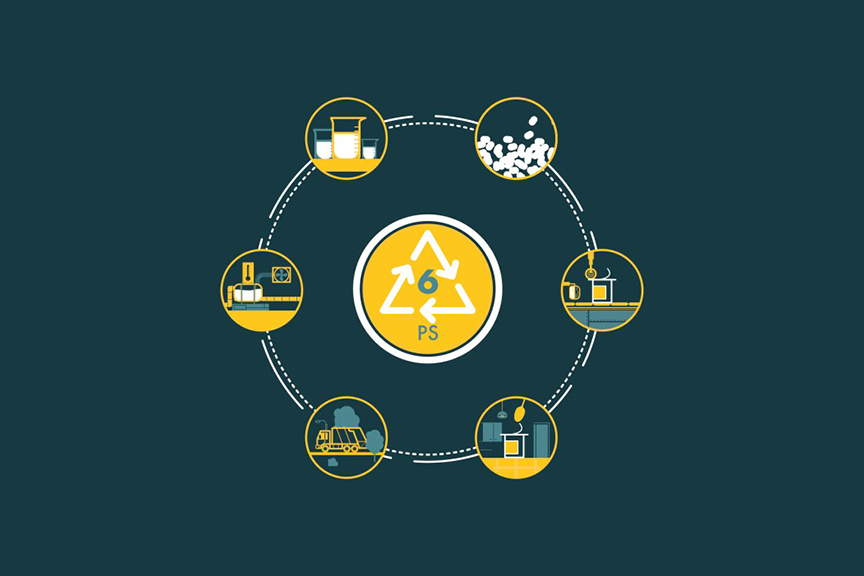
Polystyrene foam, a widely used form of plastic, finds its way into numerous aspects of our daily lives, from takeout containers to coffee cups and packaging materials. However, when it comes to recycling, polystyrene presents several challenges, leading many to wonder whether it is truly recyclable and can there be potential solutions to tackle this environmental concern.
Polystyrene, a plastic derived from styrene, is known for its versatility. Initially developed in Germany in the 1930s, this clear, hard, and brittle plastic has been used to create CD and DVD jewel cases, plastic forks, and a range of containers, including those used in the food industry.
In 1941, Dow scientist Ray McIntyre invented extruded polystyrene foam, commonly known as Styrofoam. This lightweight, waterproof material found applications in life rafts, insulation, and packaging due to its exceptional insulating properties and buoyancy.
Polystyrene’s lightweight and bulkiness make it challenging to recycle through traditional curbside programs. Additionally, the plastic’s identification code, “No. 6,” makes it less straightforward to sort and recycle compared to other plastics. Food and beverage containers made from polystyrene often end up mixed with paper, food scraps, and other plastics, further complicating the recycling process.
Most local recycling centers do not accept Styrofoam or polystyrene, requiring it to be transported to centralized facilities, increasing recycling costs and diminishing the incentive to recycle.
The recycling rate for polystyrene, according to the Alliance for Foam Packaging Recycling, is approximately 12%. However, this figure often includes scraps from the manufacturing process, which are reused immediately, painting a rosier picture of polystyrene recycling than the reality.
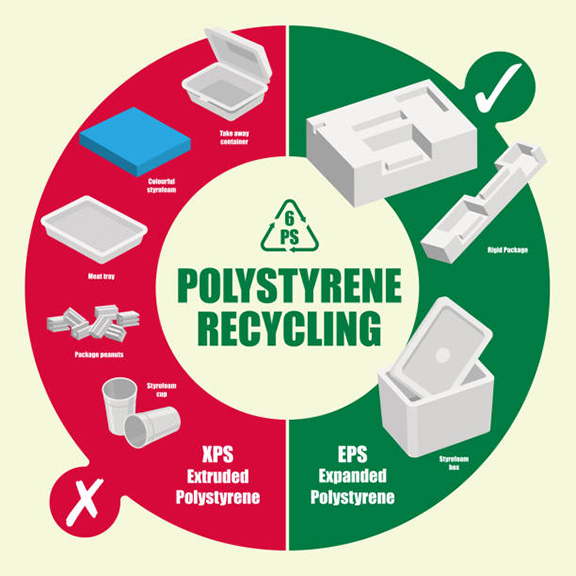
To address the challenges of recycling, various alternative methods have been explored, including reusing containers, reprocessing, and reducing bulk for more efficient transportation to recycling facilities. Additionally, thermal recycling can turn it into a valuable energy source.
Recycling polystyrene has several notable benefits, including reducing the demand for petroleum, a nonrenewable resource required for polystyrene production. It also significantly decreases litter on land and in the sea, which poses a severe threat to marine life. The reduction of marine litter and the prevention of toxic emissions from burning polystyrene underscore the importance of recycling efforts.
While recycling polystyrene remains a complex challenge, it is essential to consider the environmental impact of alternatives. For instance, paper cups with plastic coatings and ceramic containers also present sustainability challenges, emphasizing the need for careful evaluation.
Although recycling challenges exist, the benefits of recycling polystyrene are clear, including the reduction of marine litter and the conservation of nonrenewable resources. In the quest for sustainability, we must consider not only the challenges but also the broader environmental impact of alternative materials, making informed choices of using alternative products for a greener future.