Waste and recycling regulations have long been a point of contention for business owners. While many applaud rules that promote recycling and waste diversion, the constantly evolving landscape of federal, state, and local regulations can make compliance seem like an endless and challenging task, especially in recent years. In this article, we delve into three types of waste and recycling regulations that every forward-thinking business should embrace today while also anticipating future changes in this crucial arena.
Packaging Regulations: Reducing Waste at the Source
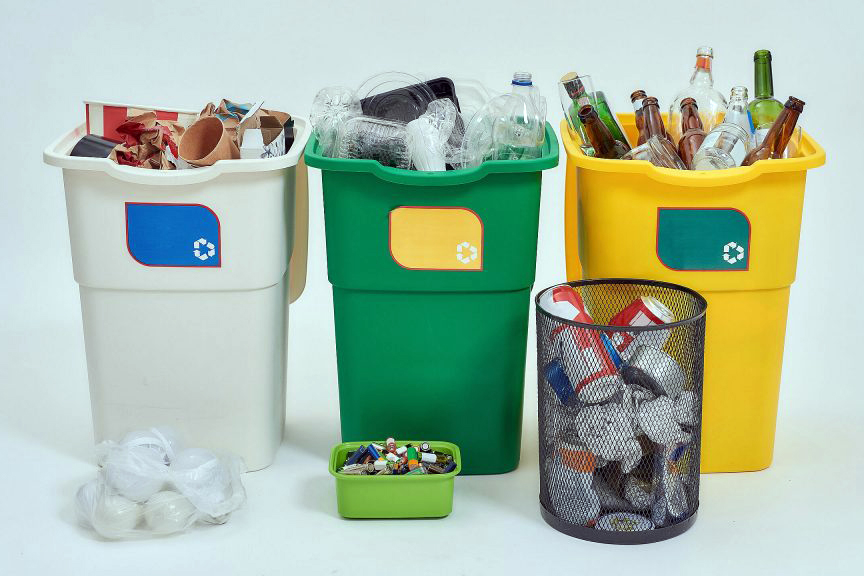
Packaging regulations are aimed at governing the production, use, and disposal of packaging materials. Their primary objective is to minimize the amount of packaging waste generated by businesses and to encourage recycling and reuse of these materials. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) reports that containers and packaging constitute nearly 30 percent of municipal solid waste, significantly contributing to landfill congestion and environmental pollution.
These regulations tackle the packaging waste problem by:
- Setting Recycling Targets: Regulations set specific targets for recycling and recovery rates, aiming to divert packaging materials from landfills.
- Mandating Recycled Content: Businesses may be required to incorporate recycled materials into their packaging, promoting sustainability.
- Promoting Reusable Packaging: Encouraging the use of reusable packaging options over single-use counterparts.
- Discouraging Single-Use Packaging: Discouraging the use of single-use packaging, which often contributes to unnecessary waste.
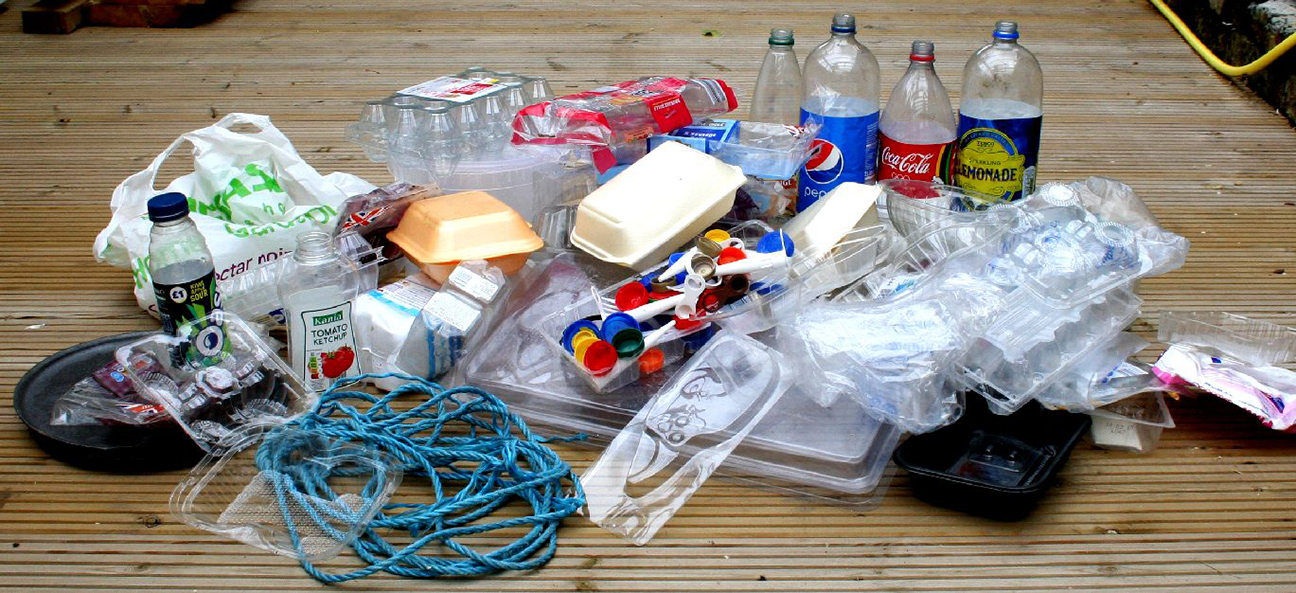

Navigating the complexities of packaging waste management is no small feat. The materials involved, including plastics, paper, glass, and metals, each come with unique recycling attributes and environmental impacts. To comply with packaging waste regulations, businesses can adopt strategies such as bulk purchasing, embracing reusable alternatives, and partnering with environmentally conscious suppliers.
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): Shifting Accountability to Manufacturers
Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) is an environmental policy approach that holds packaging producers responsible for the entire lifecycle of their products, from design to disposal. This comprehensive accountability encompasses financial and operational responsibilities, including collecting and recycling used products. EPR regulations effectively reduce waste, conserve resources, and protect the environment by compelling producers to design sustainable and recyclable products.
EPR regulations can be implemented in various ways:
- Recycling Targets: Mandating specific recycling or recovery rates that producers must meet.
- Producer Fees: Charging producers a fee for each product sold, with the proceeds funding recycling and disposal programs.
- Collective Organizations: Requiring producers to join collective organizations that manage the recycling and disposal of their products.
While EPR regulations have gained significant traction worldwide, the United States currently lacks federal-level EPR regulations, although some states have adopted such regulations for electronics.
For manufacturers, embracing EPR regulations can enhance environmental credibility, reduce long-term waste generation costs, and open doors to new business opportunities in the development of sustainable products.

Hazardous Waste Regulations: Safeguarding Health and the Environment
Hazardous waste regulations govern the generation, transportation, treatment, storage, and disposal of hazardous waste. Hazardous waste is characterized by its potential to ignite, corrode, react explosively, or release toxic fumes, posing significant risks to both human health and the environment.
These regulations play a pivotal role in:
- Preventing Harm: Protecting human health from hazardous waste-related illnesses, including cancer and respiratory problems.
- Ecosystem Preservation: Ensuring the well-being of ecosystems by preventing the release of hazardous waste.
- Compliance Enforcement: Enforcing strict rules for the handling, storage, and disposal of hazardous waste.
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) oversees and enforces hazardous waste regulations, including inspections, permits, and enforcement measures.
Effectively managing hazardous waste necessitates employee training in safe handling techniques and proper storage practices. Collaboration with experienced hazardous waste disposal experts is crucial to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. Not only does responsible hazardous waste management benefit the environment, but it also reflects a commitment to protecting local communities and maintaining a positive corporate image.
Businesses are presented with a clear call to action. Packaging regulations pave the way for sustainable practices, reducing waste and encouraging responsible disposal. Extended Producer Responsibility empowers producers to embrace accountability, driving innovation and waste reduction. Simultaneously, hazardous waste regulations safeguard both human health and the environment.
Collectively, these regulations outline a roadmap to a greener future, urging industries to harmonize with the environment while emphasizing the urgency of shared responsibility. By advocating for and complying with these regulations, businesses can work toward sustainable waste management and ensure a healthier world for future generations.