Recycling has long been championed as the poster child for responsible waste management. It’s the process of turning used items into raw materials, ready to be reborn as entirely new products. But what if we told you there’s another, often overlooked hero in the sustainability narrative? Enter “reuse.” Unlike recycling, which involves breaking items down into raw materials, reuse means giving an object a second (or even third) life, in its current form. It’s a vital choice for companies, driven by its energy-saving benefits and undeniable environmental advantages.
Reuse may seem like a simple concept, but its impact is far-reaching. Here’s why it’s gaining traction as a sustainable choice, even over recycling.
Energy Efficiency:
Perhaps the most compelling argument for reuse is its energy efficiency. Recycling typically requires significant energy to collect, transport, and process materials back into raw form. In contrast, reuse requires minimal energy. When an item is used again in its current state, it skips the energy-intensive recycling process altogether.
Reduced Carbon Footprint:
Less energy consumption translates to a reduced carbon footprint. Reuse helps lower greenhouse gas emissions associated with recycling facilities and the manufacturing of new products.
Resource Conservation:
Reuse extends the life of products and materials, reducing the demand for new resources. This not only conserves valuable raw materials but also minimizes the environmental impact of resource extraction.
Waste Reduction:
By keeping items in circulation, reuse diverts them from landfills and incinerators. This directly reduces the burden on waste management systems and minimizes the release of harmful pollutants.
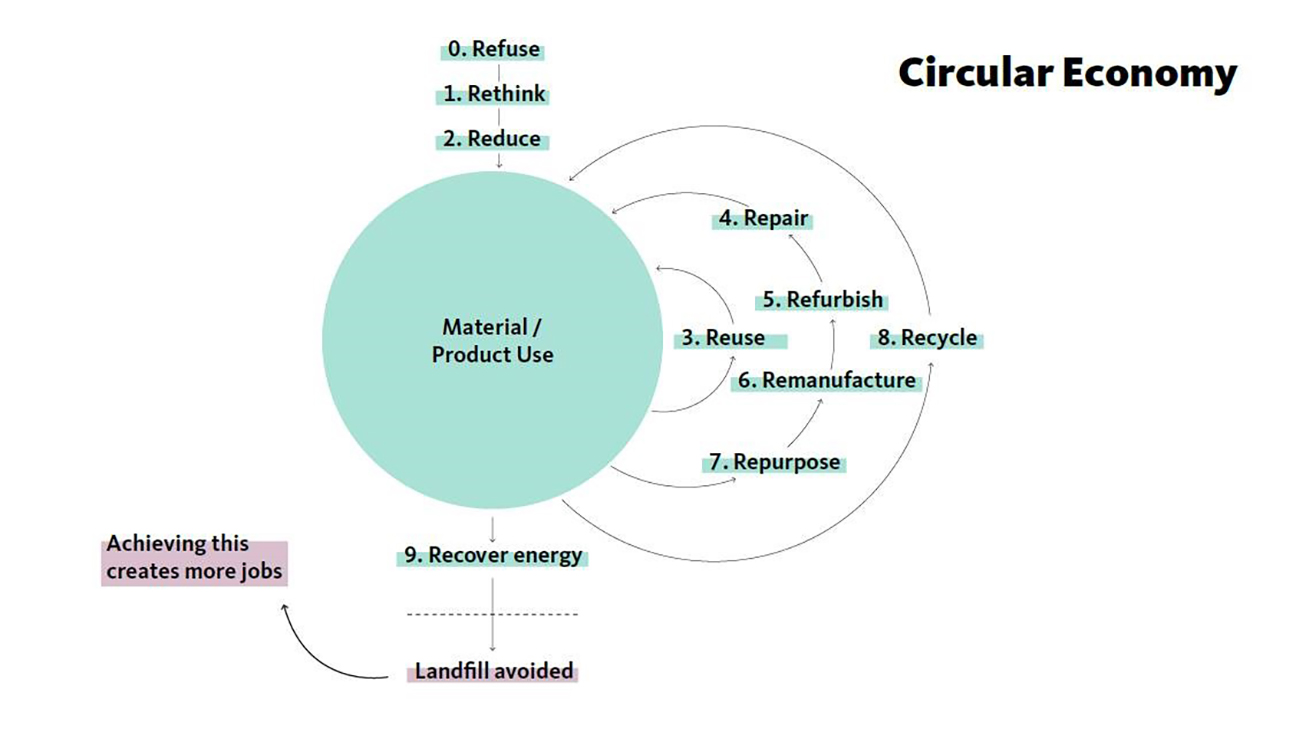
The shift toward reuse isn’t limited to individuals; businesses and industries are also recognizing its value.
Tech Giants:
Companies like Apple and Samsung offer certified refurbished products, extending the life of electronic devices and reducing electronic waste. These products are often indistinguishable from new ones and come with warranties.
Fashion Brands:
Clothing companies like Patagonia and The North Face have embraced repair and resale programs, encouraging customers to repair and resell their products instead of discarding them.
Automotive Industry:
Car manufacturers are exploring remanufactured parts and components, offering a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative to new parts.
Consumer Goods:
Various consumer goods companies are exploring reuse models, from refillable household cleaners to reusable packaging. Reuse isn’t just a smart choice; it’s a sustainability game-changer. By opting for reuse over recycling, companies can significantly reduce their energy consumption, lower their carbon footprint, conserve resources, and minimize waste.
Remanufactured Print Consumables:
The remanufacturing of ink cartridges represents a shining example of reuse in the business world. Companies like Planet Green Recycle have pioneered the art of giving ink cartridges a second lease on life. Instead of disposing of used cartridges, they collect, remanufacture, and refill them, transforming them into fully functional printing supplies. This not only extends the life of each cartridge but also significantly reduces the energy and resources required to produce brand-new ones. Remanufactured ink cartridges are not only cost-effective but also eco-friendly, offering a sustainable alternative to the constant cycle of cartridge disposal.
Reuse isn’t just a smart choice; it’s a sustainability game-changer. By opting for reuse over recycling, companies can significantly reduce their energy consumption, lower their carbon footprint, conserve resources, and minimize waste. The value of reuse lies not only in its environmental benefits but also in its potential for cost savings and innovation. It’s a win-win solution that exemplifies how conscious choices can have a profound impact on our planet’s future.