In the ever-evolving landscape of modern industry, sustainability has emerged as a core principle that transcends mere environmental compliance. Companies are now tasked with finding innovative ways to operate efficiently while also reducing their ecological footprint. Enter “Lean Manufacturing,” a systematic method designed to achieve waste minimization within manufacturing systems without compromising productivity that can profoundly impact environmental sustainability.
Understanding Lean Manufacturing:
Lean Manufacturing, often simply referred to as “Lean,” is a holistic approach to production that prioritizes the elimination of waste in all its forms. Waste, in this context, includes defects, excess processing, overproduction, waiting, inventory, moving, motion, and non-utilized talent. Lean aims to optimize processes and resources to deliver maximum value to customers while minimizing waste at every step of the manufacturing journey. Let’s examine the key principles that underpin Lean Manufacturing.
Lean places a strong emphasis on identifying and eliminating defects in the production process. This not only improves product quality but also reduces the need for rework, saving resources and reducing waste.
By streamlining processes and eliminating unnecessary steps or activities, Lean Manufacturing minimizes excess processing. This results in both time and resource savings, contributing to efficiency and sustainability.
Lean Manufacturing and Environmental Sustainability:
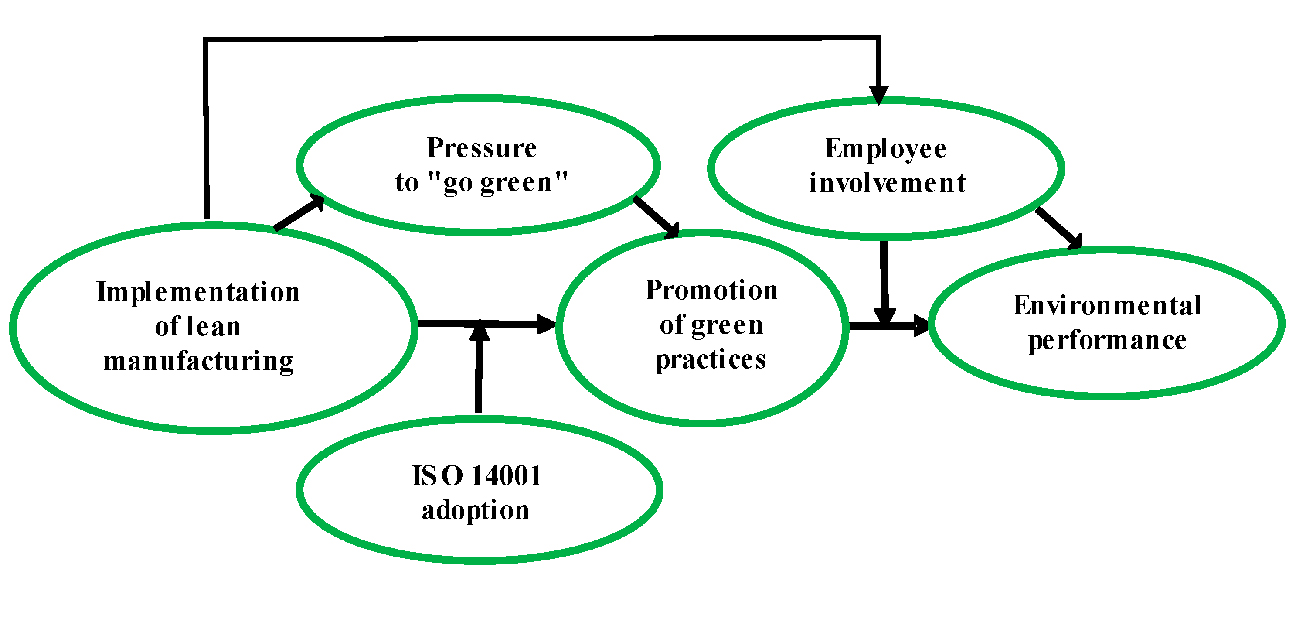
The principles of this method extend far beyond the realm of productivity. They have a profound impact on environmental sustainability, particularly through the reduction of excess processing and defects.
Lean practices, when implemented effectively, lead to reduced resource consumption. By eliminating excess processing and streamlining operations, companies can use fewer materials, energy, and water, contributing to resource conservation.
Lean principles prioritize energy-efficient processes. Companies that reduce excess processing and minimize defects often require less energy to operate, reducing greenhouse gas emissions and energy costs.
Lean significantly reduces waste generation, including hazardous waste. This minimizes the environmental impact of waste disposal and lessens the burden on landfills and waste treatment facilities.
A focus on defect reduction extends product lifecycles, reducing the need for premature replacements. This reduces the environmental impact associated with the manufacturing, transportation, and disposal of goods.
Lean Manufacturing is a transformative philosophy that aligns productivity with environmental responsibility. By eliminating waste in the form of defects and excess processing, companies can operate more efficiently while minimizing their environmental footprint. Lean principles empower organizations to embrace sustainable practices that not only benefit their bottom line but also contribute hand-in-hand to a greener, more eco-conscious future.