Counterfeit products have become a prevalent issue on e-commerce platforms, with Amazon being no exception. This growing concern impacts not only consumers but also genuine brands, and raises questions about Amazon’s responsibility in tackling this problem.
Counterfeit products thrive on Amazon, with a vast array of fake goods available to often unsuspecting consumers. According to recent statistics released by Amazon themselves, they battled 10 million counterfeit listings in 2021, up from 6 million in 2020. This surge in counterfeit items not only threatens consumer safety but also erodes trust in these platforms that continue to sell counterfeit products.
One example of this surge is the proliferation of counterfeit electronic gadgets, including counterfeit Apple AirPods and iPhone chargers, ink cartridges and even electric skateboards. These knockoff products not only fail to meet quality and safety standards but can also lead to dangerous consequences. Despite Amazon’s stated efforts to crack down on counterfeits, these products continue to sell, though Amazon says “they slip through the cracks.” It seems like a lot of cracks.

Counterfeit products pose a significant threat to consumers. Not only do they jeopardize safety, but they can also lead to frustration in getting reimbursement and consumers suffer real financial losses. Stories of consumers who received counterfeit items ranging from subpar electronics to counterfeit designer clothing and products like ink cartridges are disturbingly common. In many cases, these products fail to meet basic quality and safety standards and can pose health risks to the user and damage to the item they are applied to.
Consider the case of a consumer who purchased a supposed “genuine” cellphone battery on Amazon, only to have it explode while charging, causing injuries and property damage. Such incidents highlight the real and immediate dangers that counterfeit products, sold daily on Amazon, can pose.
Genuine brands also suffer the consequences of counterfeit products sold on Amazon. These fakes not only siphon sales from legitimate products and take away jobs, but also tarnish a brand’s reputation. Imagine a well-established brand whose product is counterfeited on Amazon, leading to dissatisfied customers receiving poor-quality imitations. This ultimately undermines the brand’s credibility and trust in the long term.
Major clothing brands such as Nike, Apple, and Louis Vuitton have initiated legal action against sellers peddling counterfeit versions of their products on Amazon. Recent lawsuits include Planet Green, Inc over false advertising and unfair competition and even the Federal Trade Commission suing Amazon over Monopoly Power, while Amazon continues selling and distributing counterfeits with straight out deception on consumers from Chinese manufacturers. Despite these legal efforts, the sheer volume of counterfeit listings makes it challenging for brands to fully protect their intellectual property and consumers from counterfeits.
Amazon claims to have made efforts to address the issue of counterfeit products on its platform. The company talks about anti-counterfeiting programs and strict policies to detect and remove counterfeit listings, though they seem minimally enforced at best. For instance, Amazon’s “Project Zero” initiative claims brands can take more direct control over their product listings to reduce counterfeits, though in cases like Royal Silk suing Amazon (https://casetext.com/case/melwani-v-amazoncom-2), even the empty promises of counterfeit control fail to get the support and protection that brand manufacturers pay Amazon for.

Additionally, Amazon has employed machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence to monitor and identify seller listings and seller accounts. When counterfeit products are reported or identified, they claim to swiftly remove them from the platform and the responsible sellers are said to face penalties, including account suspension; but Chinese counterfeit manufacturers have multiple accounts to host their listings and rarely see downtime.
While Amazon’s initiatives may seem commendable, their effectiveness remains a subject of debate. Critics argue that the platform’s sheer size and the volume of listings make it challenging to completely eradicate counterfeit products. Moreover, the allure of low-priced counterfeits often outweighs the risks for some consumers, further perpetuating the issue.
Detecting counterfeit products on a massive e-commerce platform like Amazon is not a straightforward task. One of the challenges is the dynamic nature of the counterfeit market. Sellers, especially China’s counterfeit manufacturers, frequently change their branding, packaging, and even the products themselves to evade detection.
The role of third-party sellers on Amazon adds complexity to the issue. While Amazon claims it has implemented a thorough vetting process for sellers, counterfeiters still manage to infiltrate the platform in ridiculously high numbers. The fulfillment services provided by Amazon further complicate the matter, as third-party sellers simply pay Amazon to use these services to store and ship counterfeit goods directly from Amazon’s warehouses within the US.
The legal and regulatory environment surrounding counterfeit products is complex and varies by jurisdiction. However, Amazon, like all e-commerce platforms, is bound by national and international laws and regulations. These regulations encompass areas such as intellectual property rights, trademark law, and consumer protection.
In the United States, the Lanham Act and the U.S. Copyright Act are among the primary legal tools brands use to combat counterfeit goods. Internationally, the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) and the Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) also provide a framework for protecting intellectual property rights.
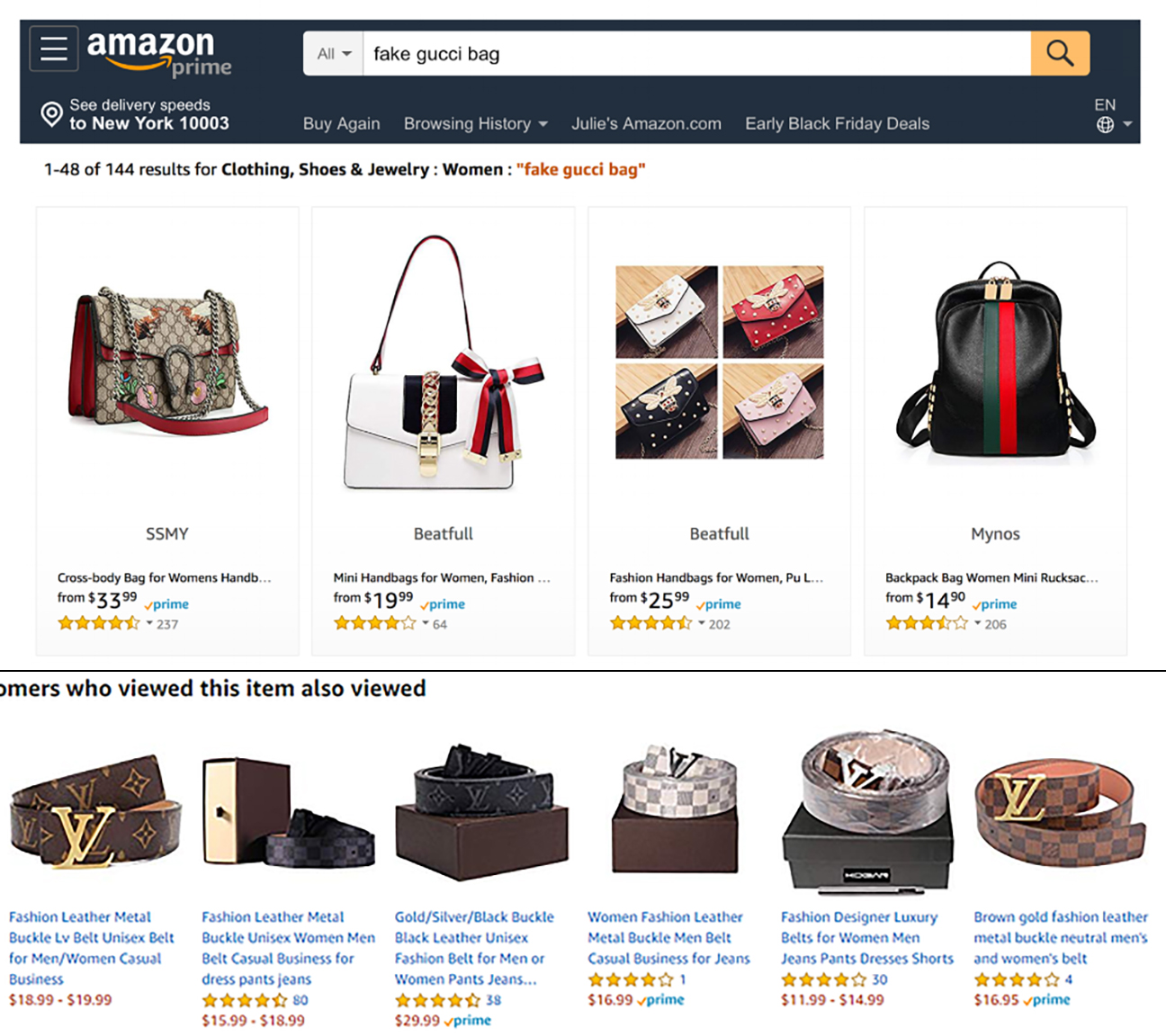
Amazon’s stated policies, though in direct opposition to many facts found, are written with an alignment to international trade regulations and the World Trade Organization’s Agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS). This global perspective highlights the issues of the complexity of tackling counterfeits, especially on a platform as extensive and seemingly unregulated as Amazon, though talk is cheap and while terminology states platforms are in compliance, counterfeit items still dominate the sales platforms.
Empowering consumers to protect themselves is crucial and awareness is virtually the only way consumers can avoid fraud. To avoid counterfeit purchases, consumers should scrutinize product listings, read reviews, and conduct due diligence on sellers. When consumers suspect they have received counterfeit goods, they must immediately report the issue to Trade Organizations and groups with political clout; then approach Amazon, demand a refund and contact their credit card company to dispute the charge.
Amazon states that it has established a dedicated “A-to-Z Guarantee” that provides consumers with a level of protection against counterfeit products – consumers need to hold them accountable to that guarantee. This guarantee allows customers to request a refund or replacement if they receive counterfeit or damaged items, though through an often straining and unresponsive process, many consumers take the loss and move on.
Neither brands nor consumers can currently trust Amazon to protect shoppers, eradicate counterfeit products or to stand behind trademarks, regardless of the claims on Amazon’s Brand Registry or any of Amazon’s anti-counterfeiting tools. Awareness is the best protection consumers currently have. The issue of counterfeit products on Amazon is a multifaceted challenge that continues to evolve. The prevalence of counterfeit goods, their impact on consumers and brands and Amazon’s limp-wristed response in challenging or even identifying counterfeits means buyers must enhance their efforts to combat counterfeits on Amazon and other platforms.
Counterfeit products not only undermine trust in e-commerce but also pose real dangers to consumers and loss to brand manufacturers and the US labor force. The responsibility to combat counterfeits rests with Amazon and the other platforms they sell on, to protect consumers, brands, and sellers. Only through collective efforts and a commitment to transparency and integrity can consumers and brands hope to be safeguarded from the sale of counterfeit products in the digital marketplace.