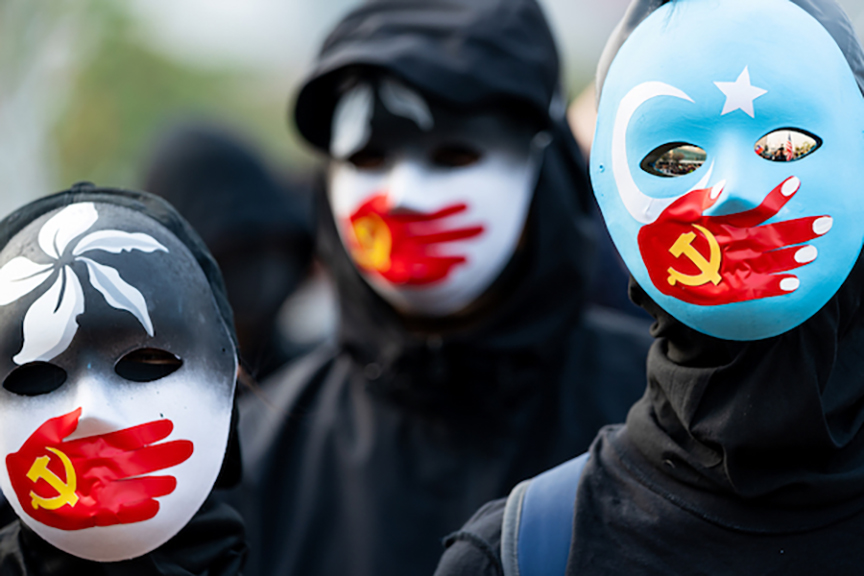
In recent years, the global community has come together to address the pressing issue of forced labor, particularly within vulnerable communities exploited for profit. A case that vividly illustrates this problem is the ongoing importation and sale of Ninestar products, a company notorious for its alleged involvement in forced labor, notably within China’s Xinjiang region. Among the platforms that have been facilitating the persistence of such injustices, Amazon stands out, potentially contributing to the perpetuation of modern-day slavery.
The U.S. government has taken a firm stance against forced labor through the Uyghur Forced Labor Prevention Act (UFLPA), adding Ninestar, a China-based printer and cartridge manufacturer, to the UFLPA Entity List. As of June 9th, 2023, the importation of Ninestar products will be deemed illegal. The allegations against Ninestar, including recruiting, transporting, and harboring forced labor from persecuted groups, represent a grave violation of human rights and have raised ethical concerns on a global scale.
Despite the efforts to combat these injustices, a troubling reality persists. Amazon, one of the world’s largest e-commerce giants, continues to list and sell Ninestar products under various brand names, effectively providing a platform for these ethically questionable products to reach unsuspecting consumers. This behavior not only contradicts the principles of social responsibility but also perpetuates an industry that thrives on the exploitation of vulnerable workers.
Ninestar, recognized as the third-largest printer and printer cartridge manufacturer globally, operates under multiple brand identities. By facilitating the sale of Ninestar products, Amazon may inadvertently be contributing to an industry that profits from modern-day slavery. The competitive pricing of these products, often fueled by unethical labor practices, creates an unjust advantage over alternatives like environmentally-friendly U.S. made remanufactured cartridges.
With its status as a dominant global marketplace, Amazon carries a heightened moral responsibility. The company’s platform has the power to either uphold ethical standards or perpetuate injustices. Given Ninestar’s inclusion on the UFLPA Entity List, Amazon’s continued facilitation of their products raises critical questions about its commitment to combating forced labor and safeguarding human rights.
As a platform that prides itself on convenience and customer satisfaction, Amazon must carefully consider the potential consequences of its actions. The importation and sale of Ninestar products could expose Amazon to not only public backlash but also legal and regulatory challenges. The ethical implications are glaring, as the company risks tarnishing its reputation as a responsible and conscientious corporate entity.
It is of paramount importance that Amazon takes proactive steps to address these concerns and uphold its commitment to ethical business practices. The company should exercise due diligence in scrutinizing the products it offers for sale, especially when allegations of forced labor and human rights abuses are involved. By maintaining Ninestar products on its platform, Amazon may inadvertently condone this grave injustice and compromise its own perceived values.
In a world where corporate social responsibility holds increasing significance, Amazon has a unique opportunity to effect positive change. Removing Ninestar products from its listings would send a powerful message against forced labor and align with global efforts to combat modern-day slavery. This action could set a precedent for other e-commerce giants, illustrating the possibility of effecting real change through responsible business practices over the quest for profit at any cost.