As our world grapples with climate change and dwindling resources, the spotlight is on the rise of the circular economy, an innovative concept geared toward a sustainable future. This transformative economic model is set to revolutionize the way we produce and consume, significantly reducing the environmental impact of consumerism by eliminating waste and optimizing resource use.
In the heart of this transition is the ink cartridge remanufacturing industry, which acknowledges the environmental challenges posed by disposable ink cartridges. To counter the growing e-waste problem, this industry is actively remanufacturing and reusing ink cartridge plastic components, mitigating the ecological footprint generated annually.
The Circular Economy Unveiled
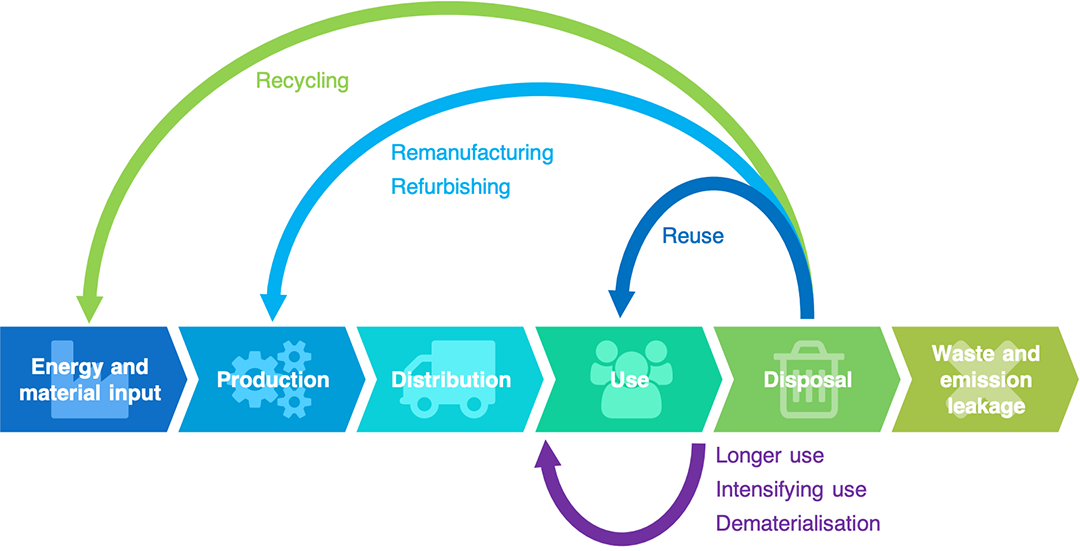
Diverging from the linear “take-make-dispose” approach, the circular economy champions principles of waste elimination and resource optimization. Products and materials are designed with durability, repairability, and recyclability in mind. Industries are prompted to reimagine their processes, emphasizing waste reduction and energy efficiency.
From sourcing sustainable materials to responsible waste management, understanding the circular economy means examining every facet of a product’s life cycle. In the automotive sector, a circular approach is gaining traction as electric vehicle manufacturers develop recyclable batteries, reducing waste and the demand for raw materials.
Taking Action in a Circular Economy
Transitioning to a circular economy necessitates collaborative efforts from individuals, businesses, and governments. Repairing products, utilizing recycled and renewable materials, and extending product lifecycles are paramount. Businesses can implement innovative practices like leasing and sharing, while consumers embrace a “make, use, return” mindset.
A zero-waste mindset plays a crucial role in minimizing landfill waste. By ensuring the proper recycling or composting of materials that cannot be repurposed, we take significant steps toward a more sustainable future.
Unleashing Value through Waste Valorization
Waste valorization is a core tenet of the circular economy. It involves repurposing waste materials into valuable components, offering an environmentally friendly alternative to disposal. Examples include the transformation of organic waste into nutrient-rich compost and the recycling of plastics, reducing the reliance on virgin materials.
The Rise of Green Consumers
With increased awareness and education, green consumers are on the rise. They prioritize products and brands committed to mitigating their environmental footprint, sparking a shift in the marketplace. From eco-friendly packaging to energy-efficient appliances, green consumers are reshaping the way we shop and pushing companies to adopt more sustainable practices.
Overcoming Challenges for a Circular Future
Transitioning to a circular economy is not without its challenges, including resistance to change and upfront costs. The pervasive availability of single-use plastic items, relentlessly marketed to consumers, underscores the urgency of addressing this issue. Governments must take a proactive role by enacting legislation, providing incentives for sustainable business practices, and launching educational campaigns to promote responsible consumption.
The circular economy is not a mere catchphrase; it’s a transformative concept with the potential to revolutionize our lifestyles, production methods, and consumption patterns. It offers a path toward a greener, more sustainable future. Our choices, from product purchases to waste management, hold the power to shape a more sustainable world for future generations. Embracing the circular economy isn’t just an option; it’s an imperative for the well-being of our planet and the legacy we leave behind.